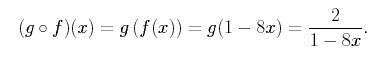Functions
Composition of Functions
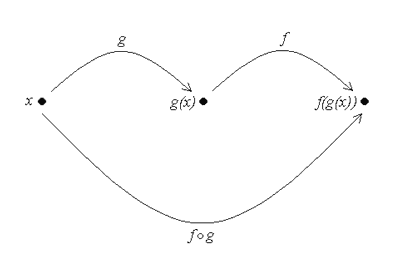
The idea behind composing functions is to take the function of another function. Many of the models you many see in the life sciences are the composition of simpler functions. Definition Let f(x) and g(x) be two functions.
The notation f (g(x)) is read as, “f of g of x.” Breaking down composite functions To break down the composite function, we work from the inside out. First, we take a value of x in the domain of g and evaluate g(x). Next, we take the value of g(x) that we just got, and substitute it into f(x). But, we can only do this if g(x) is in the domain of f. We can represent this with a diagram,
We will now look at some examples of composite functions. First, consider the functions, f(x) = 3x − 1, g(x) = x2. Using the definition of composition, we find
as follows, The domain of
consists of all x in the domain of g such that g(x) is in the domain of f . To determine the domain, we start with the inside function and work outward. The inside function is g(x), and the domain of g(x) is all real numbers. Now we need to be sure that the value of g(x) (i.e. the range of g) is in the domain of f (x). Any value of g(x), however, is in the domain of f (x) since f has domain all real numbers. Therefore, the domain of
is all real numbers. In a similar manner, we can also find
as,
For similar reasons as above, the domain of is also all real numbers.
Now consider the following functions, f (x) = 1 − 8x, g(x) = 2 / x . We find
as follows, Thus, we find
The domain of consists of all x in the domain of g such that g(x) is in the domain of f . We determine the domain by starting with the inside function and working outward. The inside function is g(x), and the domain of g(x) is {x | x ≠ 0}. Now we need to be sure that the value of g(x) (i.e. the range of g) is in the domain of f(x). Any value of g(x), however, is in the domain of f(x) because f has domain all real numbers. Therefore the domain of is {x | x ≠ 0} (i.e. all x in the domain of g such that g(x) is the domain of f). In a similar manner, we can also find as,
To find the domain we need to find all x in the domain of f such that f (x) is in the domain of g. The domain of f is all real numbers. The domain of g is {x | x ≠ 1/8 }. The range of f is all real numbers, therefore f can take on the value 1/8 and thus, we must remove it from the domain. Therefore, we conclude that the domain of is {x | x ≠ 1/8} . ***** In the next section we explore inverse functions. |
The Biology Project > Biomath > Function > Composition
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics
The University of Arizona
January 2006
Contact the Development Team
http://www.biology.arizona.edu
All contents copyright © 2006. All rights reserved.