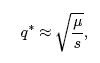Power Functions
Introduction
|
Suppose there is a single locus with two alleles, A and a, with frequencies p and q = 1 - p, respectively. We will assume that allele a is deleterious and recessive, and that mutations only occur in a forward direction at a rate of μ per generation. If s is the selection coefficient corresponding to allele a, where s = 0 implies neutrality and s = 1 implies lethality, the equilibrium frequency of allele a (given by q*) is approximated as,
where 0 < s < 1. This equation is a power function. Could you use it in the classroom or laboratory? If not, then continue with this tutorial and try out the problems at the end of the section.
***** In the next section we explore the basics of power functions. |
The Biology Project > Biomath > Power Functions > Introduction
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics
The University of Arizona
April 2007
Contact the Development Team
http://www.biology.arizona.edu All contents copyright © 2007. All rights reserved.